BEST CENTRIFUGE SUPPLIER & MANUFACTURER in CHINA
KETHINK is a one-stop centrifuge supplier, factory and manufacturer, providing most of the different types of centrifuge .
China Best Centrifuge Supplier, Manufacturer & Factory
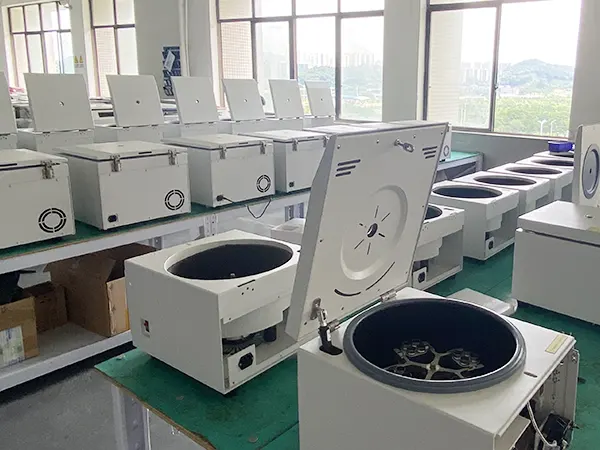
Founded in China in 2012, KETHINK has acquired a solid name in the manufacture and export of various centrifuges. KETHNK’s centrifuges are widely used in clinical, experimental, separation and purification and other fields. Certified by CE, and ISO9001 & ISO13485 listed.
We have rich experiences in production & research development for different centrifuge types. We focus on advanced technology, strict manufacturing step, and a perfect QC system.
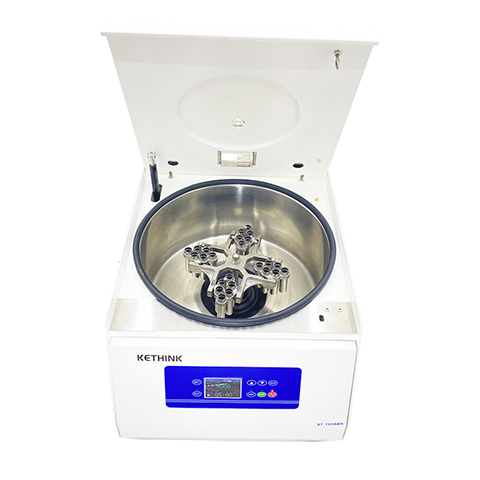
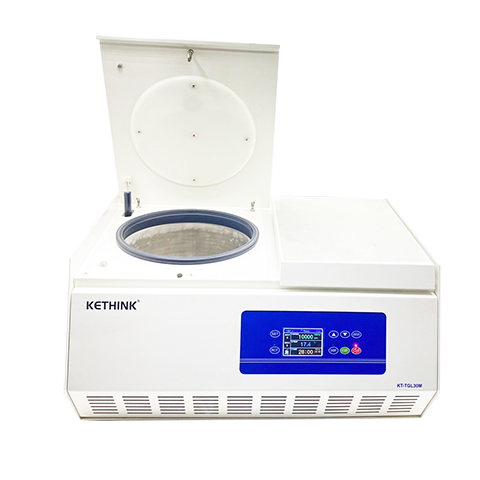
Types of Centrifuge
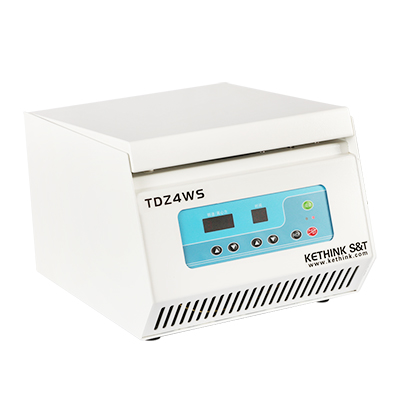
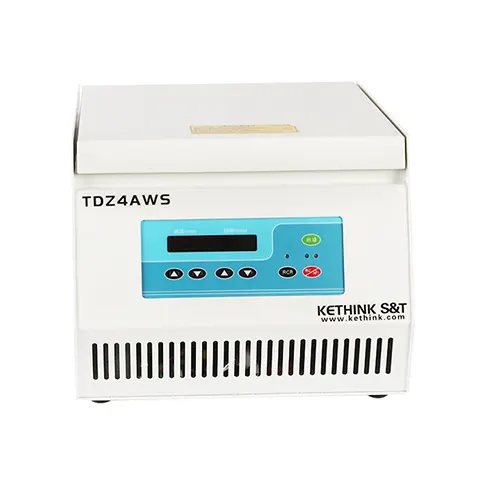
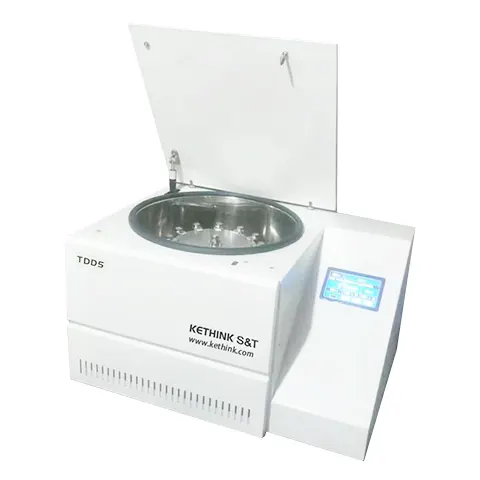
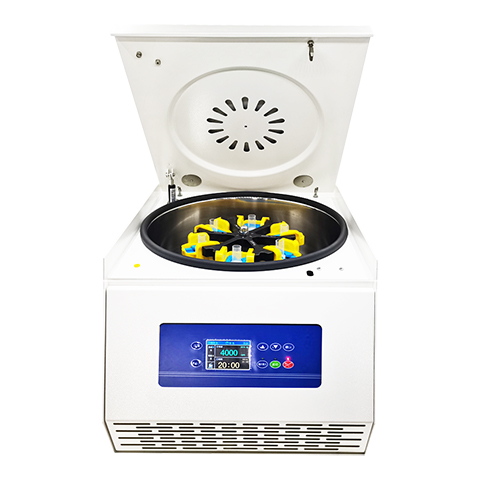
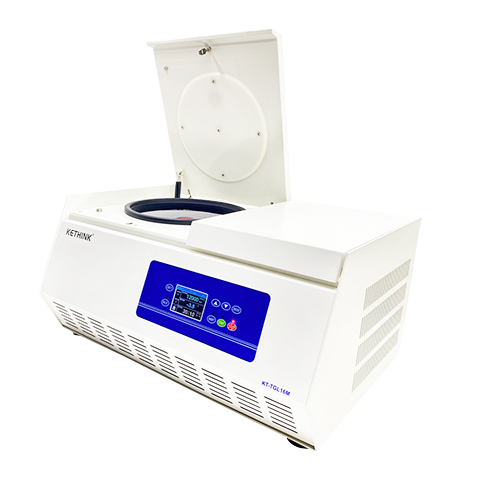
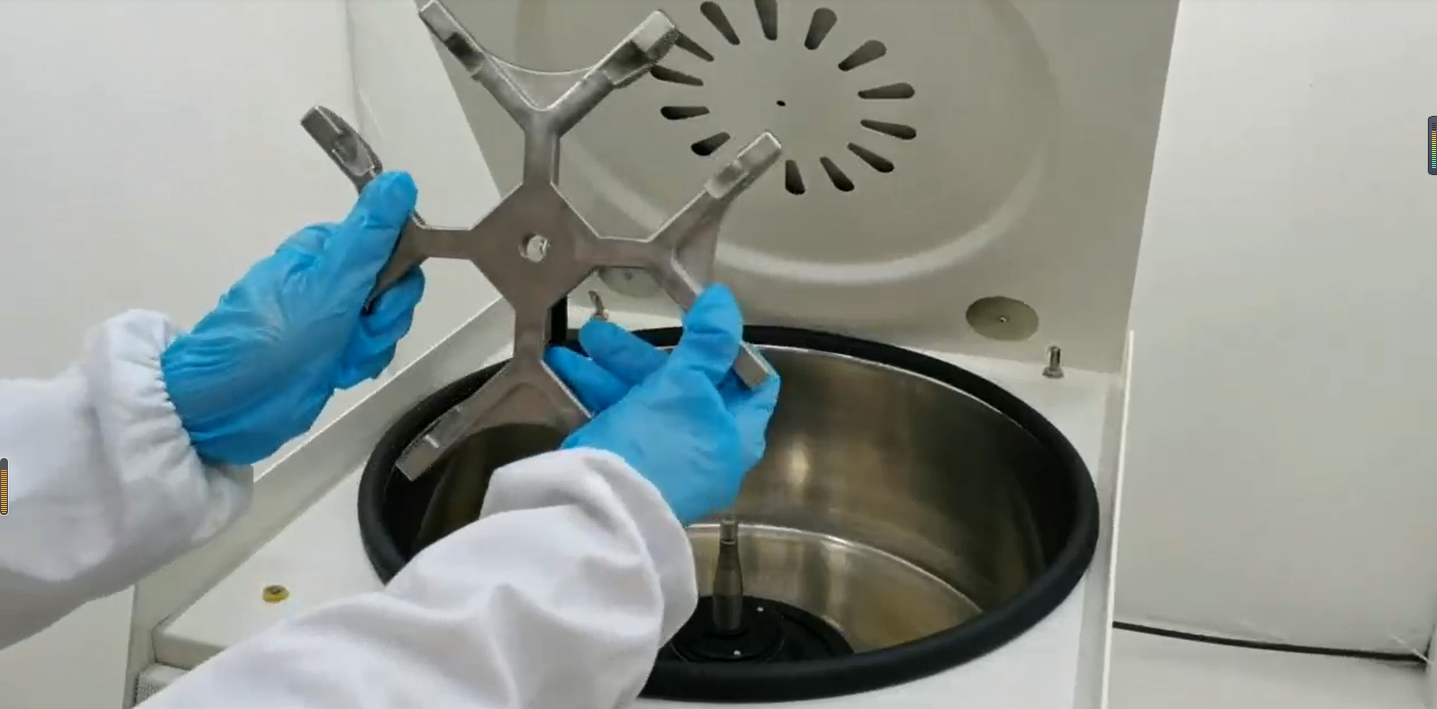
Table Top Centrifuge
Model:KT-TD5AWS
MOQ: 1 set
Type: Low Speed
Don’t you find what you are looking for?
Just tell us your detailed requirements. The best offer will be provided.
BEST SERVICES FROM CHINA CENTRIFUGE MANUFACTURER
- OEM/ODM is available, and centrifuges or rotors can be customized freely.
- There are no MOQ restrictions for retailers, wholesalers, distributors or engineering companies.
- control panel, logo,rotor customizable.
- 1-year product after-sales service: After the expiration of the warranty period of each brand of centrifuge, the maintenance will be charged.
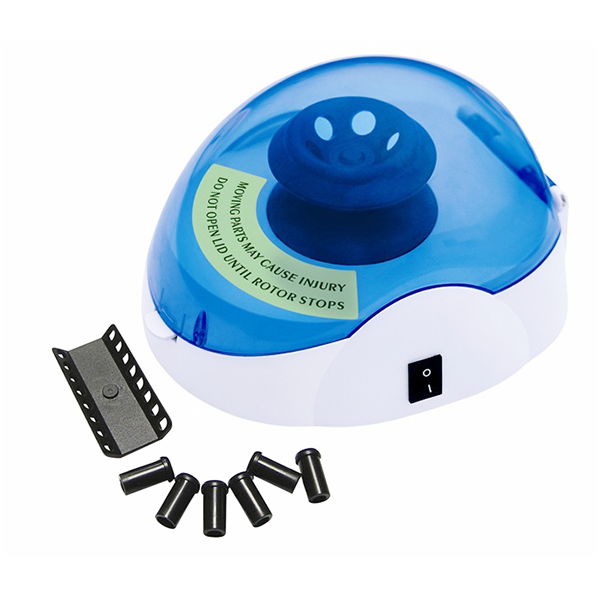
PORTABLE CENTRIFUGES
KETHINK is a portable centrifuge supplier, factory, and manufacturer, providing most of the different types of centrifuge .
- Plate Centrifuge: 96 well plate centrifuge, mini plate spinner centrifuge, microplate centrifuge.
- Micro centrifuges : Refrigerated Micro Centrifuge, Micro Hematocrit Centrifuge, Mini Microcentrifuge.
- Mini Centrifuges : Benchtop mini centrifuge, Mini spin microcentrifuge, Mini plate spinner centrifuge
China centrifuge manufacturer,factory and supplier
We can provide centrifuge solutions to do commercial projects
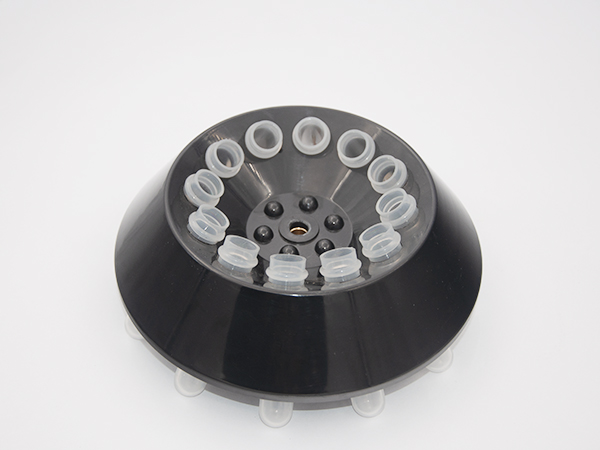
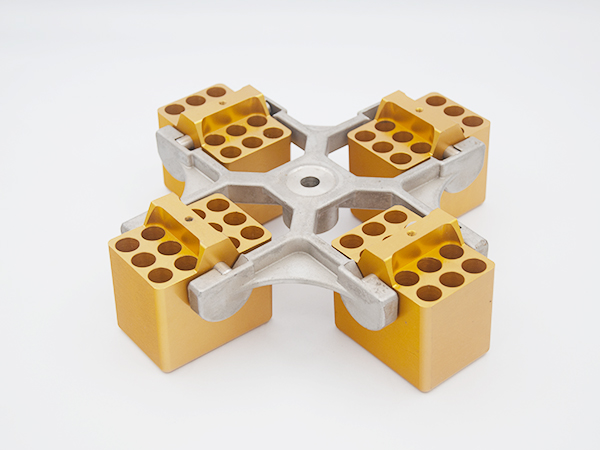
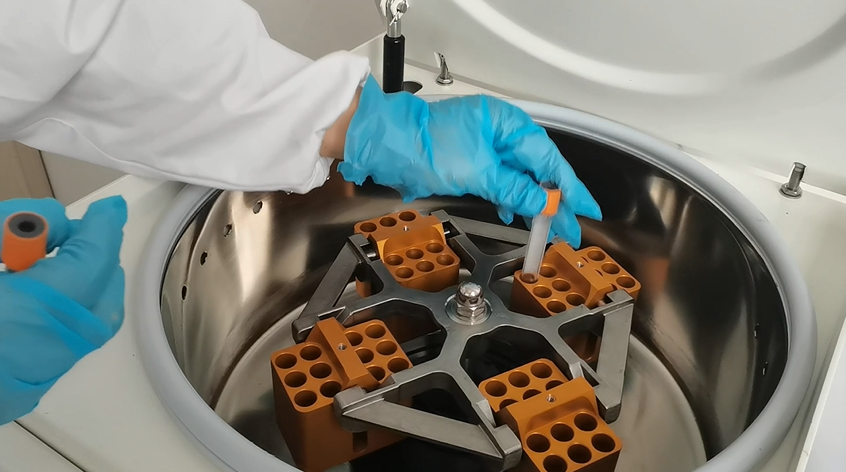
We offer a wide range of centrifuge accessories (rotors, buckets and adapters) for almost all standard laboratory applications. In addition to our standard product line, we also offer many custom and specialty application solutions. Let us know if you have a unique application and need a centrifugation solution.
A centrifuge can be described as a machine with a rapidly spinning container that applies centrifugal force to its contents. There are several types of centrifuges, which can be classified by rotor design:
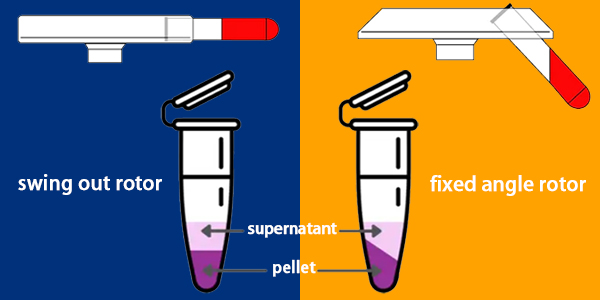
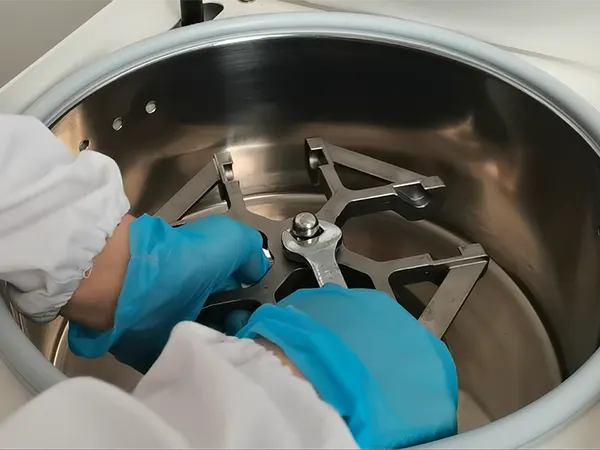
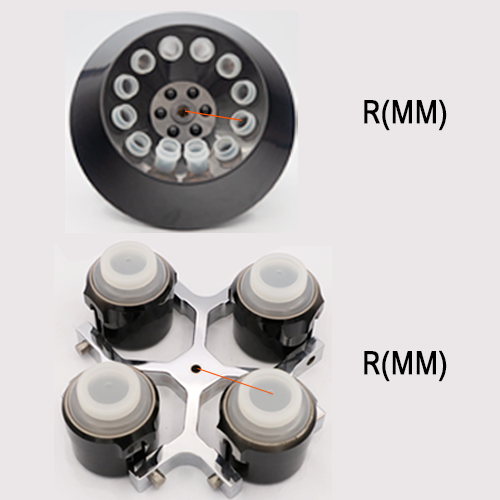
Fixed-angle rotor
The obvious advantage is that there are no moving parts in the rotor. This results in lower metal stress (longer service life), higher maximum g-forces are possible, and for many applications, faster centrifugation times can be achieved. The limited capacity (less flexibility) of fixed angle rotors is the only downside. The position of the particle is largely determined by the angle of the tube, which lies from the side to the bottom of the tube as it rotates. The tubes of most rotors have a 45° angle. The larger the angle of the tube, the tighter the pellet. A smaller rotor angle results in a more dispersed particle area.
Swing-bucket rotor
This rotor is very flexible and can use different tube formats, including SBS format plates, based on an extensive adapter system and high sample capacity. The moving swinging bucket parts cause increased metal stress on the rotor and bucket. Because the bucket weight puts the load on both pivots and grooves. Therefore, the maximum g-force of the swinging bucket rotor is limited to a lower level compared to fixed angle rotors, resulting in longer centrifugation times. Based on the swinging bucket principle, the particles are located at the bottom of the tube (the horizontal position of the tube during the run). Compared with the pellets located on the tube side, it is easier for the user to recycle.
Vertical Tube Rotor
Vertical rotors are quite specialized – they are most commonly used in ultracentrifugation for isopycnic separations, especially bands of DNA in cesium chloride. In this type of separation, the density range of the solution contains the same density as the particles of interest; therefore the particles will be oriented within this part of the gradient. Isodensity separation does not depend on the path length of the gradient, but on the runtime, which must be sufficient to orient the particles in the proper position within the gradient.
The K-factor of a vertical rotor is very low (usually in the range of 5-25), which means that the particle can only travel a short distance to reach the particle (or form a band in this case); thus the run time is minimized. Once it is determined that a vertical rotor is suitable for the end user application, volume and speed become the determining factors for which rotor to use.
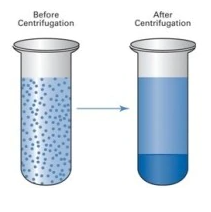
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to separate various components of a fluid. It is achieved by rotating the fluid at high speed within the container, thereby separating fluids or liquids of different densities from solids.
It works by moving denser matter and particles radially outward. At the same time, less dense objects are displaced and moved to the center. In laboratory centrifuges that use sample tubes, radial acceleration causes denser particles to settle to the bottom of the tube, while less dense material rises to the top.
Centrifuges are used to separate particles suspended in liquids based on particle size and density, media viscosity and rotor speed.
In a solution, gravity causes particles with a density higher than the solvent to sink, while particles with a density lower than the solvent float to the top. Centrifugation utilizes even minute density differences to separate particles in solution.
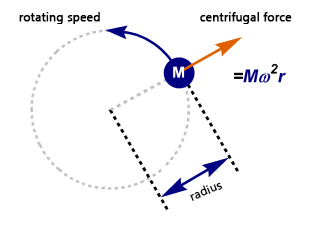
As the rotor rotates around the central axis, it creates centrifugal force that keeps the particles away from the axis of rotation. If the centrifugal force exceeds the buoyancy of the liquid medium and the frictional force created by the particles, the particles will settle.
Various laboratory scale centrifuges are used in chemistry, biology, biochemistry and clinical medicine. For separation and suspension and immiscible liquids. They vary widely in speed, capacity, temperature control and other features. Laboratory centrifuges typically accept a range of different fixed-angle and swing-bucket rotors capable of carrying different numbers of centrifuge tubes and rated for a specific maximum speed.
Controls range from simple electronic timers to programmable models capable of controlling acceleration and deceleration rates, operating speed and temperature status. Regional rotors and continuous flow systems are capable of handling large and larger sample volumes, respectively, in laboratory-scale instruments.
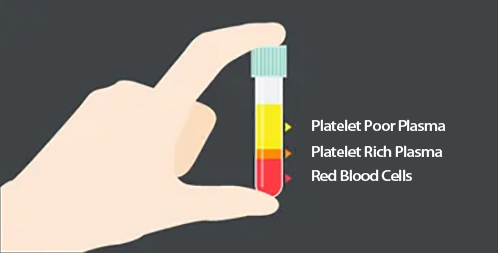
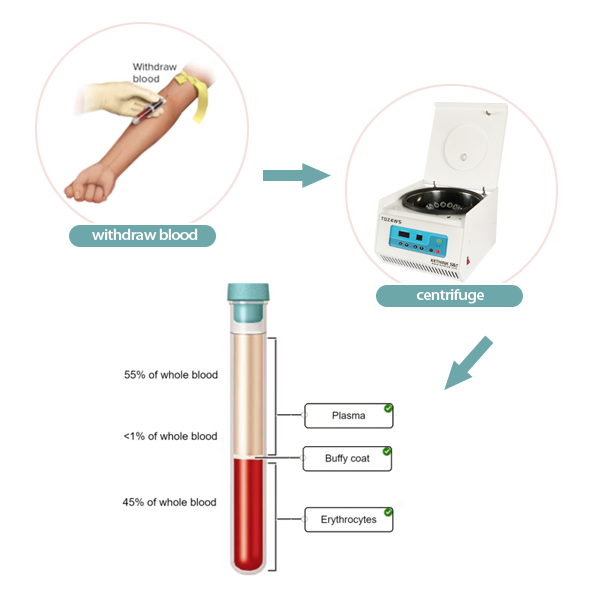
Another application of laboratory centrifuges is blood separation. Blood is separated into cells and proteins (RBCs, WBCs, platelets, etc.) and serum. Deoxyribonucleic acid preparations are another common application in pharmacogenetics and clinical diagnostics. Purify the DNA sample and prepare the DNA for isolation by adding buffer and then centrifuging it for a certain amount of time. The blood waste is then removed and another buffer is added and spun in the centrifuge again. Once the blood waste is removed and another buffer is added, the particles can be suspended and cooled. The protein can then be removed and the entire mass can be centrifuged again and the DNA can be completely isolated. Medical and biological laboratories use specialized cytocentrifuges to concentrate cells for microscopy.
Related Reading: Centrifuge wiki
Centrifuge tubes for use with centrifuge instruments are available in glass and plastic types. Tubes are also available in a variety of volume capacities, RCF ratings, cap types, velocity resistance, sterile/non-sterile formats. as well as some characteristic scales to aid in volume measurement are available
Centrifuge tubes are a must for sample separation, stratification or density gradient separation. They find a variety of applications in biology (especially cell culture and microbiology), chemistry, clinical healthcare and the wider industrial setting.
PS: We mainly provide plastic centrifuge tubes.
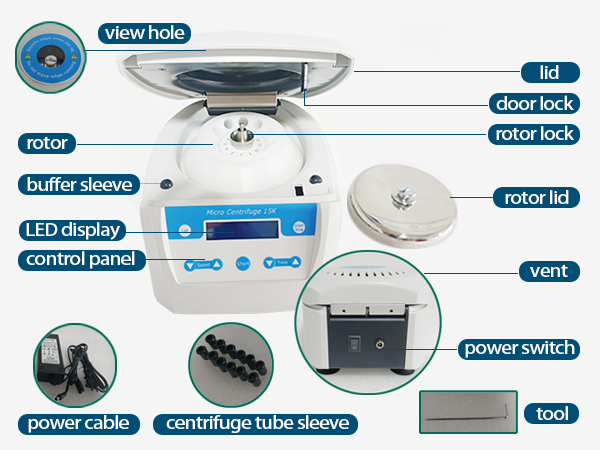
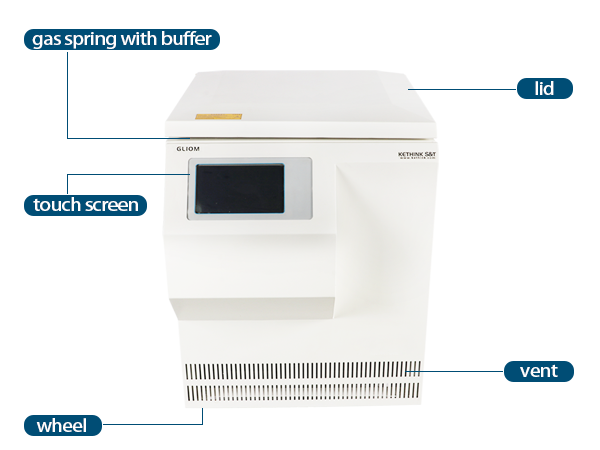
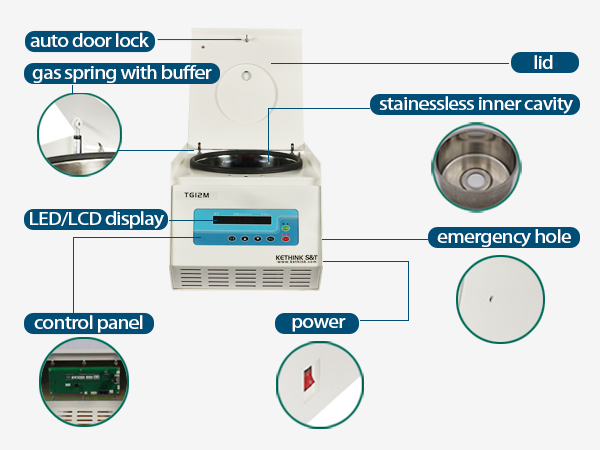
Centrifuge Diagram
Centrifuges are ideal separation equipment in the fields of biology, medicine and pharmaceuticals. The working principle of the centrifuge is mainly divided into two parts: the centrifugal part and the freezing part. The basic structure of the centrifuge includes: drive system, control system, refrigeration system, safety protection system, rotor, shell, cover, inner tank. Speed, centrifugation time and centrifugation temperature can be controlled by the program of the control system.
What We Can Offer You…
Competitive Price
Our centrifuge has an absolute advantage in price. Under the same quality, our price is generally 10%-30% lower than the market.
After-sale
We provide 1 year guarantee policy. Within warranty period, maintenance costs due to product quality will be on our account.
Best Quality
We have rich experience in the manufacture, design and application of centrifuge, and served more than 210 customers from worldwide.
Testing Service
All products have been EMC tested to ensure the operator’s safety and reliability of the centrifuge in the working process.
Shipping
We have experienced shipping forwarder, available to do shipping by air express, sea, and even door to door service.
Our Certificates
As a professional centrifuge manufacturer, our factory has passed CE, and ISO9001:2010, ISO13485 listed.
What Our Clients Say
300+
Happy Clients
I was skeptical about this after reading the reviews but once I got it I realized that others probably just weren’t balancing their centrifuges. If you balance it properly, it’s perfectly quiet. The only complaint I have is the speed knob isn’t secured well so if you turn it past the max setting it’ll spin around in the housing, it’s just a minor inconvenience.
I use this for backup on PRP treatments purposes, but at this moment works very well without problems running for 10 minutes maybe 10 times a day at 4000RPM
Stays in place, spins well but you cannot set in between the marks. I need to set on 700rpm for prf and you cannot set it there. Your options are in 500rpm increments. Nice machine for the price. I will need to spend more for what I want.
Blogs
Frequently
Asked
Questions
If you cannot find an answer to your question in our FAQ, you can always contact us
and we will be with you shortly.













































































































.jpg)